The role of NADH and FADH2 is to donate electrons to the electron transport chain. They both donate electrons by providing an hydrogen molecule to the oxygen molecule to create water during the electron transport chain. NADH is a product of both the glycolysis
Glycolysis
Glycolysis (from glycose, an older term for glucose + -lysis degradation) is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate, CH3COCOO + H. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy compounds ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and N…
What happens to the electrons carried by NADH and FADH2?
Jun 23, 2020 · What do NADH and FADH2 donate? The electron transport chain is located on the inner membrane of the mitochondria, as shown below. The electron transport chain contains a number of electron carriers. These carriers take the electrons from NADH and FADH2, pass them down the chain of complexes and electron carriers, and ultimately produce ATP.
What are the commercial applications of NADH and FADH2?
The electron transport chain is a series of electron transporters embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane that shuttles electrons from NADH and FADH2 to molecular oxygen. In the process, protons are pumped from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space, and oxygen is reduced to form water.
Why does FADH2 produce 2 ATP during the etc?
The role of NADH and FADH2 is to donate electrons to the electron transport chain. They both donate electrons by providing an hydrogen molecule to the oxygen molecule to create water during the electron transport chain. NADH is a product of both the glycolysis and Kreb cycles. FADH2 is only produced in Krebs cycle.
What is the electron donor in the electron transport chain?
May 30, 2020 · Regarding this, what happens to electrons carried by NADH and fadh2? Basically, the NADH and FADH2 molecules are affixed with electrons and are transferred to the inner membrane of the mitochondria. They travel down the electron transport chain, releasing the electrons that they once had. The end result is loads of energy, approximately 34 ATP (energy …
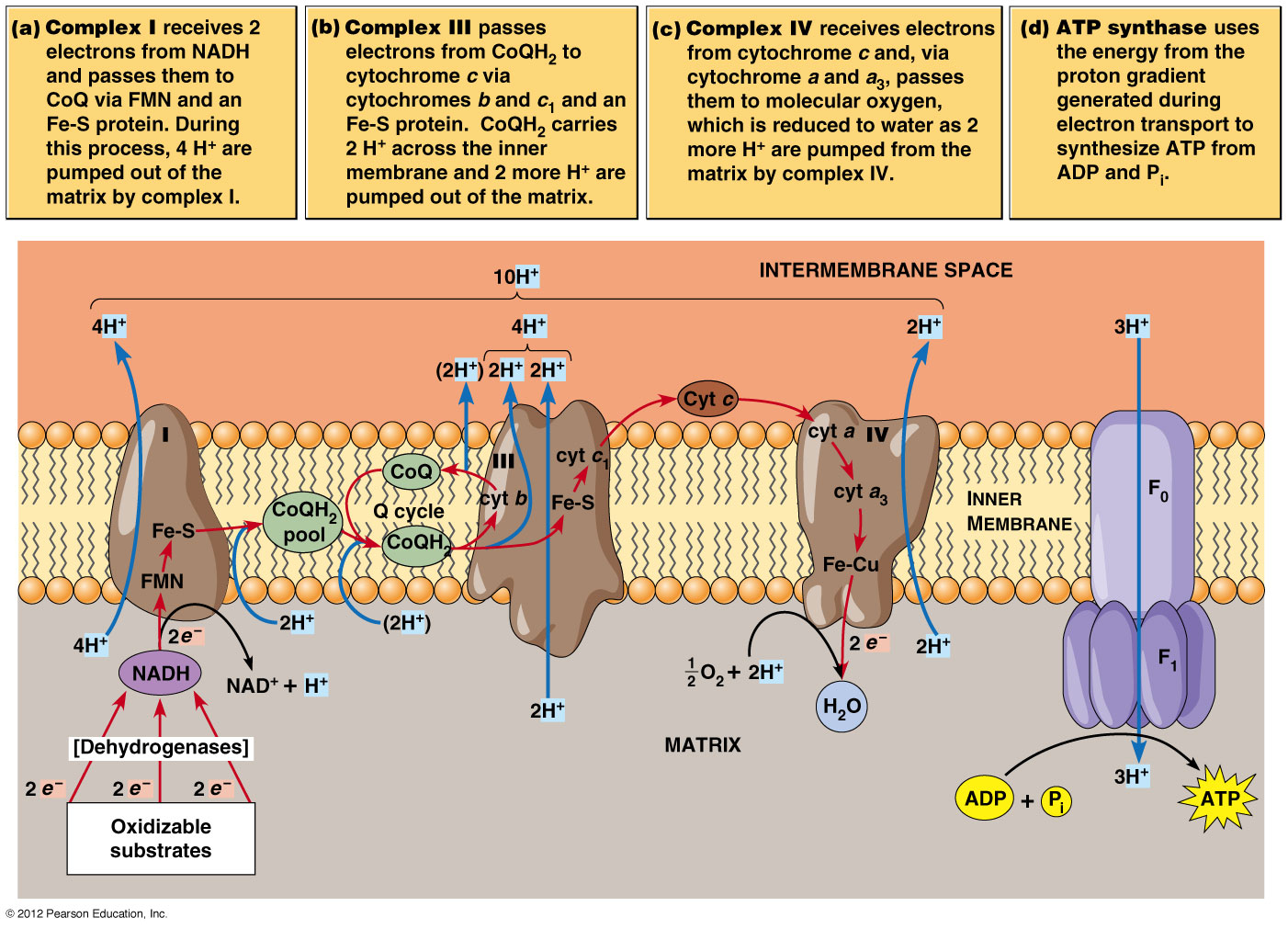
How do NADH and FADH2 donate their electrons?
NADH and FADH2 made in the citric acid cycle (in the mitochondrial matrix) deposit their electrons into the electron transport chain at complexes I and II, respectively. This step regenerates NAD+ and FAD (the oxidized carriers) for use in the citric acid cycle.
Do NADH and FADH2 donate their electrons to the chain?
NADH and FADH2 are both electron carriers that donate their electrons to the electron transport chain. The electrons ultimately reduce O2 to water in the final step of electron transport.
When NADH donates electrons to the electron transport chain?
NADH is the electron donor in this system. It initiates the electron transport chain by donating electrons to NADH dehydrogenase (blue). NADH donates two electrons to NADH dehydrogenase. At the same time, the complex also pumps two protons from the matrix space of the mitochondria into the intermembrane space.
What happens to the electrons released from NADH and FADH2?
High-energy electrons are released from NADH and FADH2, and they move along electron transport chains, like those used in photosynthesis. The electron transport chains are on the inner membrane of the mitochondrion. As the high-energy electrons are transported along the chains, some of their energy is captured.Mar 5, 2021
Does NADH contribute more electrons than fadh?
FADH2 produces less ATP then NADH because FADH2 is reduced more. FADH2 produces less ATP then NADH because NADH has more energetic electrons.
Which compounds donate electrons to the electron transport chain?
NADH and FADH2 are both electron carriers that donate their electrons to the electron transport chain.
How is NADH an electron donor?
NADH is a strong electron donor: because its electrons are held in a high-energy linkage, the free-energy change for passing its electrons to many other molecules is favorable (see Figure 14-9). It is difficult to form a high-energy linkage. Therefore its redox partner, NAD+, is of necessity a weak electron acceptor.
What happens to NADH in the electron transport chain?
In complex I, electrons are passed from NADH to the electron transport chain, where they flow through the remaining complexes. NADH is oxidized to NAD in this process. Complex II oxidizes FADH, garnering still more electrons for the chain.
Is FADH2 an electron donor?
Electrons enter the ETC from an electron donor, such as NADH or FADH2 which are generated during a variety of catabolic reactions, like and including those associated glucose oxidation .Jun 2, 2019
How are the electrons in NADH and FADH used to make ATP during cellular respiration?
NADH and FADH2 molecules formed during Glycolysis and Krebs Cycle carry their electrons to the electron transport chain. The electron transport chain creates a proton gradient that ultimately leads to the production of a large amount of ATP.Jun 22, 2019
What is the role of NADH and FADH2 in oxidative phosphorylation?
During oxidative phosphorylation, electrons derived from NADH and FADH2 combine with O2, and the energy released from these oxidation/ reduction reactions is used to drive the synthesis of ATP from ADP.
How many electrons does NADH and FADH2 carry?
Explanation: Both NADH and FADH2 donate two electrons to the electron transport chain, so theoretically they should make the same amount of ATP.
How do NADH and FADH2 work together?
The role of NADH and FADH2 is to donate electrons to the electron transport chain and to act as an electron carrier, which carries electrons released from different metabolic pathways to the final process of energy production, i.e., the electron transport chain. They both donate electrons by providing a hydrogen molecule to the oxygen molecule to create water during the electron transport chain. Thus both NADH and FADH2 are vital in all metabolic processes. The difference between NADH and FADH2 is that NADH is a coenzyme derived from vitamin B3 or niacin whereas FADH2 is a coenzyme derived from Vitamin B2 or riboflavin.
What is the difference between NADH and FADH2?
The difference between NADH and FADH2 is that NADH is a coenzyme derived from vitamin B3 or niacin whereas FADH2 is a coenzyme derived from Vitamin B2 or riboflavin.
What are the two coenzymes?
A coenzyme is an organic non-protein molecule which is relatively small in size and has the ability to carry chemical groups between enzymes and act as an electron carrier. NADH (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide) and FADH2 (Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide) are two main coenzymes utilized in almost all biochemical pathways. They act as electron carriers and participates in oxidation-reduction reactions of reaction intermediates. NADH is a derivative of Vitamin B3 ( Niacin/Nicotinamide) while FADH2 is a derivative of Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin). This is the key difference between NADH and FADH2.
What is FADH2?
FADH2 is the reduced form of flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD). FAD is synthesized from riboflavin and two molecules of ATP. Riboflavin is phosphorylated by ATP to produce riboflavin 5′-phosphate (also called flavin mononucleotide, FMN). FAD is then formed from FMN by the transfer of an AMP molecule from ATP.
What is NADH made of?
What is NADH? NADH is synthesized from Vitamin B3 (Niacin) and is a coenzyme composed of ribosylnicotinamide 5′-diphosphate coupled to ad enosine 5′-phosphate. It serves as an electron carrier in many reactions by alternatively converting to its oxidized ( NAD+) form and the reduced (NADH) form.
Where is NADH produced?
NADH is produced in the cytosol as well as in the mitochondria. The mitochondrial membrane is impermeable to NADH, and this barrier distinguishes between cytoplasmic and mitochondrial NADH stores. In commercial applications, NADH is administered orally in order to combat fatigue as well as during energy deprived syndromes and metabolic disorders.
What is the role of NADH in glycolysis?
This role of NADH is involved in the processes of glycolysis, TCA cycle and in the electron transport chain where NADH is one of the electron donors.
Web Link
2.5 ATP/NADH and 1.5 ATP/FADH2 are produced in the electron transport chain. Some resources will say 3 ATP/NADH and 2 ATP/FADH2, but these values are generally less accepted now.
Link
ETC Animation – http://www.science.smith.edu/departments/Biology/Bio231/etc.html
Videos
Electron Transport Chain – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1engJR_XWVU&feature=related
How are NADH and FADH2 related quizlet?
The role of NADH and FADH2 is to donate electrons to the electron transport chain. They both donate electrons by providing an hydrogen molecule to the oxygen molecule to create water during the electron transport chain. NADH is a product of both the glycolysis and Kreb cycles. FADH2 is only produced in Krebs cycle.
What is the primary similarity between FADH2 and NADH?
Similarities Between NADH and FADH Both contain an adenine nucleotide. They carry hydrogen and electrons. Also , both of them can take up two electrons. Both carry electrons for the production of ATP during oxidative phosphorylation.
How do FADH2 and NADH function similarly?
Functions. FADH2 and NADH are created from FAD and NAD+ through reduction-oxidation reactions in the Krebs cycle during respiration as seen below: As they are shuttled away, these two compounds are used to move electrons into the electron transport chain, the final stage of respiration.
What is the function of NADH?
NADH: High energy electron carrier used to transport electrons generated in Glycolysis and Krebs Cycle to the Electron Transport Chain.
Why is NADH better than FADH2?
FADH2 produces less ATP then NADH because NADH has more energetic electrons. FADH2 produces less ATP then NADH because NADH is reduced more. Correct answer: FADH2 produces less ATP then NADH because the electrons for FADH2 are dropped off at the second protein of the electron transport chain.
Why does NADH have more energy?
NADH is more energetic because it holds more bonds, therefore more energy is required to keep this molecule intact. So when trying to break the bond, it would require more energy to break, and therefore it is also more stable then NAD+.
What is the disadvantages of anaerobic exercise?
A disadvantage of the anaerobic energy system is that energy stores are depleted quickly. Anaerobic metabolism also causes hydrogen ions to build up in the muscle tissues and lactic acid to accumulate in the blood, which causes the “burn” you feel in your muscles.
Popular Posts:
- 1. why don't people donate blood
- 2. how to donate hair from home
- 3. how do you donate platelets
- 4. where can we donate used toys in virginia
- 5. where to donate men's dress clothes
- 6. where do you go to donate sperm
- 7. where to donate stuffed animals in houston
- 8. how to get paid to donate sperm
- 9. where to donate used coloring books
- 10. where to donate clothes for interviews kennewick