How many valence electrons are in C2H4?
Apr 07, 2022 · Step 1: How many atoms do we have in an ethylene molecule? 2 Carbon and 4 Hydrogen. Hydrogen is the first element in the periodic table, therefore it has only one valence electron. In the case of carbon, we have four valence electrons each. ∴ the total number of valence electrons in one molecule of C2H4 = 2*4+1*4 =12.
Why does NH2 have 2 unpaired electrons?
Nov 28, 2018 · How many electrons do two ethylene monomers () share to form a covalent bond? 1 2 3 4 - 11659630
Why does NH2 have a-1 formal charge?
Here we assign one of the electrons of the electron pair in a single metal-metal bond to each of the metal centres e.g. (CO)5Mn Mn(CO)5 1e 1e 5x2+7+1=18 5x2+7+1=18 Metal-metal double, triple and quadruple bonds are treated in an analagous fashion by assigning 2, 3 or 4 electrons respectively to each metal.
What is the shape of C2H4?
It only has one pair of electrons that it can use to bond to the metal - any other lone pairs are pointing in the wrong direction. Some ligands, however, have rather more teeth! These are known generally as multidentate or polydentate ligands, but can be …
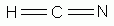
How many electrons does NH3 donate?
When neutral Lewis base ligands (like NH3) are considered they are viewed as neutral molecules with 2 electrons for donation to the metal.
How many electrons does each ligand donate?
Ligands are considered neutral in charge, and may donate either 2, 1 or zero electrons to the bond. For example, ligands such as CO and NH3 are considered to have filled valence and contribute 2 electrons.Aug 15, 2020
How many electrons does donate?
Electrons donated by common fragmentsLigandElectrons contributed (neutral counting)Electrons contributed (ionic counting)CR224Ethylene22cyclopentadienyl56benzene666 more rows
How do you determine the number of electrons in a ligand donation?
Electron countingDetermine the oxidation state of the transition metal and the resulting d-electron count. ... Determine the number of electrons from each ligand that are donated to the metal center.Add up the electron counts for the metal and for each ligand.Feb 3, 2021
How many electrons does a PPh3 ligand donate?
DONOR-PAIR METHOD Tantalum often forms the +5 oxidation state, and iridium is fine with a +1 oxidation state. Cp is C5H5 , which as a 5-electron donor is C5H−5 , cyclopentadienyl anion. CO and PPh3 are both 2-electron σ donors and π acceptors.May 1, 2018
How do you calculate electrons?
Multiply the element's atomic number by the number of atoms of this type (see Step 1) in the molecule. Repeat for all elements in the molecule, then add up all the products to calculate the number of electrons. In the first example, the number of electrons in KNO3 equals (19 x 1) + (7 x 1) + (8 x 3) = 50.Apr 26, 2018
What is an x2 ligand?
For example, if a Z ligand is accompanied by an L type, it can be written as X2. Examples of these ligands are Lewis acids, such as BR3.
What is the 16 electron rule?
Diamagnetic organometallic complexes of transition metals may exist in a significant concentration at moderate temperatures only if the metal's valence shell contains 16 or 18 electrons.
How do you calculate number of neutrons?
Subtract the atomic number from the atomic mass. Since the vast majority of an atom's mass is made up of its protons and neutrons, subtracting the number of protons (i.e. the atomic number) from the atomic mass will give you the calculated number of neutrons in the atom.
Which of the following is 3 electron donor ligand?
In an alternative description, nitric oxide serves as a 3-electron donor, and the metal-nitrogen interaction is a triple bond.
What do you mean by 18 electron rule?
18 electron rule : How to count electrons. The rule states that thermodynamically stable transition metal organometallic compounds. are formed when the sum of the metal d electrons and the electrons. conventionally considered as being supplied by the surrounding ligands equals 18.
What is the 28th electron?
Nickel atoms have 28 electrons and the shell structure is 2.8. 16.2.
How many valence electrons does hydrogen have?
Hydrogen is the first element in the periodic table, therefore it has only one valence electron. In the case of carbon, we have four valence electrons each. ∴ the total number of valence electrons in one molecule of C2H4. = 2*4+1*4 =12.
How many electrons does one carbon atom lack?
Here, we can see that one carbon atom has its octet fulfilled (the Octet rule has been discussed before). But, the other central carbon atom lacks two electrons. So, what we can do is, we can take those electrons from the bottom and place them in the center between the two C atoms.
How many electrons are in the valence shell of an element?
If we see the last group, we can find out that all the elements are inert gases having eight electrons in their valence shells (except He which has two). The atoms of the main groups tend to gain more electrons to attain the same valency of eight. This is known as the octet rule or octet fulfillment.
What are the electrons in an atom?
Valence electrons. An atom has a nucleus that is surrounded by negatively charged electrons which are present in different levels or shells. The outermost shell is known as the valence shell and the electrons present in that shell are known as valence electrons.
What does a bonding orbital do?
The 𝝅 bonding orbital will see higher electron density which will hold the atoms together via nuclei attraction. The anti-bonding 𝝅*orbital will see a larger distance of electron density, therefore, weakening the bond and causing repulsion. The 𝝅CC stands for Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital or HOMO.
What is it called when two or more atoms come close?
And this whole process of two or more atoms coming close and deciding to stay together is known as chemical bonding .
What type of bonding is found in carbon?
Chemical Bonding in Hydrocarbons. Carbon has a covalent nature when it comes to bonding with hydrogen and this leads to the formation of the different types of hydrocarbons that we see. From simplest ones like methane and benzene to some of the complex ones like natural rubber, we deal with several HCs in our daily lives.
What are the molecules that surround the central metal ion?
The molecules or ions surrounding the central metal ion are called ligands. The nature of ligands. Simple ligands include water, ammonia and chloride ions. What all these have got in common is active lone pairs of electrons in the outer energy level. These are used to form co-ordinate bonds with the metal ion.
Which ion forms a co-ordinate bond with the nitrogen atom?
Each of the lone pairs on the nitrogen can form a co-ordinate bond with the iron(II) ion - holding it at the centre of the complicated ring of atoms. The iron forms 4 co-ordinate bonds with the haem, but still has space to form two more - one above and one below the plane of the ring.
What are some examples of bidentate ligands?
The two commonly used examples are 1,2-diaminoethane (old name: ethylenediamine - often given the abbreviation "en"), and the ethanedioate ion (old name: oxalate).
Why do you only use 4 lone pairs of chloride ions?
Because chloride ions are bigger than water molecules, you can't fit 6 of them around the central ion - that's why you only use 4. Only one of the 4 lone pairs on each chloride ion is shown. The other three are pointing away from the copper ion, and aren't involved in the bonding. That gives you the complex ion:
What is the bonding of complex ions?
A complex ion has a metal ion at its centre with a number of other molecules or ions surrounding it. These can be considered to be attached to the central ion by co-ordinate (dative covalent) bonds. (In some cases, the bonding is actually more complicated than that.)
Why does the complex ion have a co-ordination number of 6?
The interesting bit is the other position. Overall, the complex ion has a co-ordination number of 6 because the central metal ion is forming 6 co-ordinate bonds.
Why is the 3+ charge on aluminum?
Because of the movement of electrons towards the centre of the ion, the 3+ charge is no longer located entirely on the aluminium, but is now spread over the whole of the ion. Because the aluminium is forming 6 bonds, the co-ordination numberof the aluminium is said to be 6.
Why is NH2 reactive?
Because it is very reactive , it does not hang around for any appreciable amount of time, and quickly bonds with other chemicals through the nitrogen atom. NH2 can also be the NH2- or “amide anion” with has two, unpaired electrons and a single, negative charge.
Which is more activating, NH2 or NR2?
NR2 is more activating than NH2, this is because although NH2 is activating, the hydrogen atoms attached to nitrogen are -I groups and hence slightly reduce the activating ability. When the Hydrogen atoms were replaced by alkyl groups, alkyl groups being +I groups, increase the activating ability. 3.8K views. ·.
What does the N-H bond mean?
Meaning in N-H bond, since N is more electronegative than H, the N owns both electrons and H owns 0. Formal charge assumes equal sharing but Oxidation assumes more electronegative owns both (these are two extremes, and may not represent reality, but the assumptions are very useful) Back to the formal charge of NH2.
Why is 1/2 bonding electrons equal?
That is why the term 1/2 bonding electrons appears in the formula: Because equal sharing means owning only half the electrons in a bond.
How many valence electrons does N have?
atomic N has 5 valence electron, if molecular N has 4 valence electrons, then 5–4 = +1 meaning N has lost ownership of an electron when it bonded and therefore has +1 formal charge. N bonds with 2 hydrogens, and is most stable with a full valence shell/ full octet.
What is the most stable configuration an atom can achieve?
all atoms bond to complete their valence shell, as a full shell or full octet is the most stable (lowest energy) configuration an atom can achieve. Once N bonds with other atoms how many of the 8 electrons does N own?
What is steric crowding?
One other thing, steric crowding means that an incoming group does not go between two groups already there. In other words, if OH and NH2 are meta to each other, the incoming group is not going to go in the 2 position to give 1 OH, 2 Z, 3 NH2.
Popular Posts:
- 1. why is there a weight requirement to donate blood
- 2. how much can you donate to church without receipts
- 3. what to donate to food banks
- 4. hoq much money can you make when donate sperm
- 5. how to know if you can donate blood
- 6. where can i donate used socks for the homeless
- 7. where to donate money to help iraqi people
- 8. how much do you get payed to donate plasma
- 9. how to donate money anonymously
- 10. how to donate money to chkd vie evite?