Why donate blood?
Blood types determine who you can give blood to and receive blood from. Which type of donation is best for you is determined by your blood type, as well as patient need. Read more to find out what makes your blood type special:
What are the rules for donating blood?
Your blood type determines who you can donate blood to, and whose blood you can receive. People with O-negative blood, for example, can give blood to recipients of any blood type. But, they can only receive blood from O-negative donors. The opposite is true for people with an AB-positive blood type — their donations can only be used for patients who are AB-positive, but …
What tests are done to evaluate donors?
There are actually three tests that are done to evaluate donors. They are blood type, crossmatch, and HLA testing. This blood test is the first step in the process of living donation and determines if you are compatible or a “match” to your recipient. Blood Typing. There are …
What is the most common blood type to donate?
Blood Components Blood Types Blood Type Compatibility Whose type can you match? Donors with type O- blood are universal red cell donors whose donations can be given to people of all blood types.Donors with types AB- and AB+ blood are universal plasma donors, while patients with type AB+ are universal red cell recipients because they can receive red cells from all types.
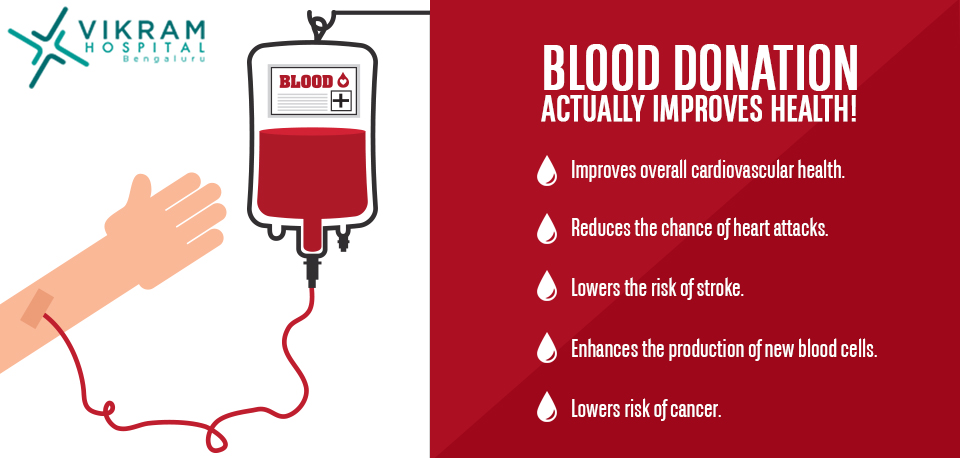
What determines blood donation?
To determine if you are eligible to donate we will: Ask about medicines you are taking or have taken. Ask about your risk for infections that can be transmitted by blood—especially AIDS and viral hepatitis. Take your blood pressure, temperature and pulse. Take a blood sample to be sure your blood count is acceptable.
Is O+ or O universal donor?
Although the blood type O+ can donate blood to all positive blood types (A+, B+, AB+, and O+), it is not a universal donor. Blood type O- is the universal blood donor, meaning that people with this blood type can donate blood to all other types with a lower risk of causing serious reactions.Jan 20, 2022
What are the 3 rarest blood types?
What are the rarest blood types?O positive: 35%O negative: 13%A positive: 30%A negative: 8%B positive: 8%B negative: 2%AB positive: 2%AB negative: 1%
What blood can not be donated?
You have Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, HIV/AIDS, or may have been exposed to these diseases via sexual contact. Hepatitis B and C and HIV/AIDs are diseases that can be passed on via blood transfusion, and therefore individuals who suffer from these diseases are ineligible to donate blood.Jan 15, 2021
Why is O negative so rare?
Only 7% of the population have O negative blood. Due to the its versatility for transfusions, it is in high demand. In an emergency, it is the blood product of choice. For example, just one car accident victim can require up to 100 units of O neg.
What's the golden blood type?
Rh null blood groupThe golden blood type or Rh null blood group contains no Rh antigens (proteins) on the red blood cells (RBCs). This is the rarest blood group in the world, with less than 50 individuals having this blood group.
What is the rarest blood type?
type ABIn the U.S., the blood type AB, Rh negative is considered the rarest, while O positive is most common.May 18, 2020
Who can receive O+ blood?
What are the major blood types?If your blood type is:You can give to:You can receive from:O PositiveO+, A+, B+, AB+O+, O-A PositiveA+, AB+A+, A-, O+, O-B PositiveB+, AB+B+, B-, O+, O-AB PositiveAB+ OnlyAll Blood Types4 more rows
What type of blood donation is most needed?
A+ is a common blood type which makes it the most needed blood for transfusions, so you may be asked to donate whole blood. Whole blood donors are eligible to give blood every 8 weeks. Platelets are another way to maximize your donation as an A+ blood type.
What is the healthiest blood type?
Of the eight main blood types, people with type O have the lowest risk for heart disease. People with types AB and B are at the greatest risk, which could be a result of higher rates of inflammation for these blood types. A heart-healthy lifestyle is particularly important for people with types AB and B blood.
What does blood type say about you?
People with type O blood have the lowest risk of heart disease while people with B and AB have the highest. People with A and AB blood have the highest rates of stomach cancer. People with type A blood can have a harder time than others managing stress because they often produce more of the stress hormone cortisol.Aug 13, 2020
How do I find out my blood type without a test?
Many people don't know their blood type. Here's how to find out yoursAsk your parents or doctor.Blood draw.At-home blood test.Blood donation.Saliva test.Jul 18, 2020
Is Golden blood actually gold?
Golden blood is not actually golden in colour, but it is actually the nickname for Rhnull, the world's rarest blood type.Jan 20, 2022
Why do they check your elbows when donating plasma?
Because arteries have higher blood pressure than veins, a puncture can lead to bleeding into the arm tissues around the puncture site. The signs of an arterial puncture include a faster blood flow and lighter-than-usual color of blood running through the tubes to the machine collecting your plasma.
What medical conditions disqualify you from donating plasma?
People can't donate if they have or had tuberculosis, heart disease (and currently taking medication for it), sickle cell anemia, certain types of cancer, or malaria (contracted in the past three years or travelled to an endemic area in the past year).Nov 12, 2019
Why can't family members donate blood to each other?
Family blood donation is generally discouraged as they are often first time or infrequent donors and do not have a safety history established. Additionally, mothers may have antibodies that react against RBC, leukocyte, platelet, or HLA antigens expressed on neonatal cells.
What percentage of the population has O blood?
Is one of the rarest blood types — only 6.6% of the US population has type O- Is a universal donor, meaning anyone can receive type O- blood products Is an ideal whole blood or double red blood cell donor. Your blood type is constantly needed, so please come in and donate as frequently as…. Read More.
What is the ABO type?
Your ABO type is based on the presence or absence of two antigens (A and B) on the surface of red blood cells. There are four ABO types: A, B, AB and O. Your blood type is also determined by Rh status: Rh+ or Rh-. That leaves us with eight possible blood types: A+.
What is the most common blood type?
The most common blood type in the population is type O. The next most common is blood type A, then B, and the rarest is blood type AB. The blood type of the donor must be compatible with the recipient. The rules for blood type in transplantation are the same as they are for blood transfusion. Some blood types can give to others and some may not.
How many antigens are there in the body?
Antigens are proteins on the cells in the body. Out of over 100 different antigens that have been identified, there are six that have been shown to be the most important in organ transplantation. Of these six antigens, we inherit three from each parent.
Can you give blood to someone with blood type O?
Some blood types can give to others and some may not. Blood type O is considered the universal donor. People with blood type O can give to any other blood type .
How to contact Canadian Blood Services?
You can call us toll free at 1 888 2 DONATE (1-888-236-6283) and a customer service representative will be happy to assist you. You can still donate blood without your Canadian Blood Services donor card since your donor information is on file.
What is the purpose of whole blood?
Every component has a job to do…. Whole Blood is made up of four separate components that can be transfused separately or together to treat various conditions. Red blood cells carry oxygen to the organs and tissues and removes carbon dioxide through the lungs. It is used during emergencies, surgeries and cancer treatments.
What are the functions of blood cells?
Every component has a job to do… 1 Red blood cells carry oxygen to the organs and tissues and removes carbon dioxide through the lungs. It is used during emergencies, surgeries and cancer treatments. 2 White blood cells protect the body from infection. They can also carry viruses and bacteria and, for this reason, are removed from any donated blood. 3 Plasma is a liquid component that carries nutrients to all parts of the body and carries waste products out of the body, acting like a cell transportation system. It is also rich in vital proteins used to treat patients undergoing extensive surgery or trauma, and patients with bleeding disorders. 4 Platelets provide the basis for clotting, which helps control bleeding. It is used to treat patients with bleeding disorders and cancer.
Why are platelets important?
Platelets provide the basis for clotting, which helps control bleeding. It is used to treat patients with bleeding disorders and cancer. All our blood cells are produced by our bone marrow - our body’s blood cell factory.
What is the function of plasma in the body?
Plasma is a liquid component that carries nutrients to all parts of the body and carries waste products out of the body, acting like a cell transportation system.
What is the RH factor?
Everyone has a type, and you belong to one of four: O, A, B and AB. An additional factor — the ‘Rh factor’ — determines whether your type is positive or negative. When you donate, we test your blood to identify exactly which type you belong to. This is important because a recipient’s blood type determines what blood type they can receive.
How to determine blood type?
Blood typing is determined by the molecules on the surface of the red blood cells (RBCs). In general, we can classify someone’s blood type by the absence or presence of A or B antigens and Rh factor on the surface of blood cells.
What are the blood groups?
The most commonly recognized blood groups are A positive, A negative, B positive, B negative, AB positive, AB negative, O positive, and O negative. The positive or negative sign next to the blood groups is known as the Rhesus (Rh) factor. The Rh factor is an inherited protein that can be found on the surface of the red blood cell.
What happens if your blood type is negative?
If your blood type is negative, then your blood cells lack the Rh protein. Although Rh positive is the most common blood type, having a Rh-negative typing does not indicate illness and usually doesn’t affect your health.
What is the difference between a positive and negative rh factor?
A person with the Rh positive factor will not make anti-Rh antibodies. Those with Rh negative factor will produce the antibodies. Therefore, someone with Rh+ blood can receive both Rh+ and Rh- transfusions, but those with Rh- can only receive Rh- blood.
How much blood volume do you need to donate?
In order to donate blood you must have at least 3400 mL of blood volume. Blood volume is determined by body weight and height, and individuals with low blood volumes may not tolerate losing so much blood.
How often can you donate blood?
Most healthy individuals will have no problem donating blood, and can do it as often as once every eight weeks. However, there are a select few who are not able to donate their blood, and the reasons why may surprise you.
Can you donate blood with Coumadin?
Those who have a health condition where their blood doesn't clot normally, or are on anticoagulant medications such as Coumadin (warfarin), should not donate blood as they may have excessive bleeding where the needle was placed. However, according to the ARC they are not automatically disqualified from donating blood.
How long after getting a tattoo can you donate blood?
Due to concerns about hepatitis, in Georgia, Idaho, Maryland, Massachusetts, Nevada, New Hampshire, New York, Pennsylvania, Utah, Wyoming, and the District of Columbia donors are asked to wait a year after getting a tattoo and a year after getting a piercing from a “questionable source” before donating blood.
How long do you have to wait to donate blood?
If they lived in a malaria-risk country for more than five years, they are asked to wait three years after returning to the U.S. before donating blood.
Can you donate blood after taking antibiotics?
However, even in the case where the infection is transmissible through blood, individuals are allowed to donate blood after they have finished their course of oral antibiotics, even if the last pill was taken on the day of the donation.

Popular Posts:
- 1. how can i donate my eggs
- 2. how do i donate to mindy mccready kids
- 3. where to donate frozen food near me
- 4. what is the max you can donate to a presidential campaign
- 5. family life cycle stage who donate to children hosptials
- 6. why can t you donate blood
- 7. where to donate gently used toys
- 8. where to donate prom dresses in berwick pa
- 9. where to donate furniture in chicago
- 10. where to donate old computers and printers