How do electrons pass from one molecule to another?
Dec 07, 2021 · The electron transport chain is a series of molecules that accept or donate electrons easily. By moving step-by-step through these, electrons are moved in a specific direction across a membrane. The movement of hydrogen ions are coupled with this. This means that when electrons are moved, hydrogen ions move too. Anne ⭐ Answeregy Expert
What is ETC (electron transport chain)?
Dec 20, 2021 · The two molecules generated by the Krebs cycle that pass their high-energy electrons to the electron transport are NADH and FADH2. Explanation: The kreb's cycle gives NADH and also the another hydrogen carrier which is termed as FADH2.During the process of the electron transport chain, one NADH gives rise to electrons and also the hydrogen ions, …
How many H+ ions are pumped across the inner membrane?
Jun 05, 2012 · coenzymes NAD and FAD that are attached to the cristae of the mitochondria. The reduced NAD and FAD donate the electrons of the hydrogen atoms they are carrying to the first molecule in the...
How are electrons transferred from NADH to FADH?
Removing 2 H atoms from substrate, delivering 2 electrons and one proton to NAD+, and releasing the remaining proton to the surrounding solution What is the process in which high energy electrons transferred from the substrate to NAD+ are passed down the ETC to oxygen, therefore powering ATP synthesis
What is the electron transport chain?
The electron transport chain is also called the Cytochrome oxidase system or as the Respiratory chain. The components of the chain include FMN, Fe–S centers, coenzyme Q, and a series of cytochromes (b, c1, c, and aa3). The energy derived from the transfer of electrons through the electron transport chain is used to pump protons across ...
How does ATP produce electrons?
The production of ATP is coupled to the transfer of electrons through the electron transport chain to O2. The overall process is known as oxidative phosphorylation. Protons flow down their electrochemical gradient through the membrane-bound ATP synthase. The flow of protons through the ATPase allows the enzyme to synthesize ATP.
How is ATP produced?
ATP is generated as a result of the energy produced when electrons from NADH and FADH2 are passed to molecular oxygen by a series of electron carriers, collectively known as the electron transport chain ( ETC). The electron transport chain is also called the Cytochrome oxidase system or as the Respiratory chain.
What is the final step of cellular respiration?
The electron transport chain is the final and most important step of cellular respiration. While Glycolysis and the Citric Acid Cycle make the necessary precursors, the electron transport chain is where a majority of the ATP is created. It has an important role in both photosynthesis and cellular respiration.
Why are NADH and FADH2 energy rich?
The NADH and FADH2 formed in glycolysis, TCA cycle and fatty acid oxidation are energy-rich molecules because they contain a pair of electrons that have high transfer potential.
Where is the respiratory chain located?
Location of ETC. The respiratory chain is located in the cytoplasmic membrane of bacteria but in case of eukaryotic cells it is located on the membrane of mitochondria.
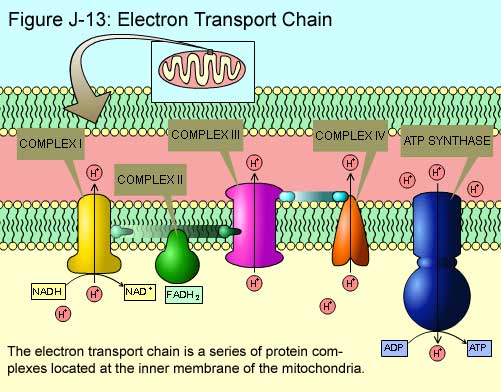
How Energy Is Made
The First Steps of Cellular Respiration
- The first step of cellular respiration is glycolysis. Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasmand involves the splitting of one molecule of glucose into two molecules of the chemical compound pyruvate. In all, two molecules of ATP and two molecules of NADH (high energy, electron carrying molecule) are generated. The second step, called the citric acid cycle or Krebs cycle, is when pyruvate is tr…
Protein Complexes in The Chain
- There are four protein complexes that are part of the electron transport chain that functions to pass electrons down the chain. A fifth protein complex serves to transport hydrogen ionsback into the matrix. These complexes are embedded within the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Complex I
- NADH transfers two electrons to Complex I resulting in four H+ ions being pumped across the inner membrane. NADH is oxidized to NAD+, which is recycled back into the Krebs cycle. Electrons are transferred from Complex I to a carrier molecule ubiquinone (Q), which is reduced to ubiquinol (QH2). Ubiquinol carries the electrons to Complex III.
Complex II
- FADH2 transfers electrons to Complex II and the electrons are passed along to ubiquinone (Q). Q is reduced to ubiquinol (QH2), which carries the electrons to Complex III. No H+ions are transported to the intermembrane space in this process.
Complex III
- The passage of electrons to Complex III drives the transport of four more H+ions across the inner membrane. QH2 is oxidized and electrons are passed to another electron carrier protein cytochrome C.
Complex IV
- Cytochrome C passes electrons to the final protein complex in the chain, Complex IV. Two H+ ions are pumped across the inner membrane. The electrons are then passed from Complex IV to an oxygen (O2) molecule, causing the molecule to split. The resulting oxygen atoms quickly grab H+ions to form two molecules of water.
ATP Synthase
- ATP synthase moves H+ ions that were pumped out of the matrix by the electron transport chain back into the matrix. The energy from the influx of protonsinto the matrix is used to generate ATP by the phosphorylation (addition of a phosphate) of ADP. The movement of ions across the selectively permeable mitochondrial membrane and down their electrochemical gradient is calle…
Sources
- "Electron Transport in the Energy Cycle of the Cell." HyperPhysics, hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/Biology/etrans.html.
- Lodish, Harvey, et al. "Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation." Molecular Cell Biology. 4th Edition., U.S. National Library of Medicine, 2000, www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK21528/.
Popular Posts:
- 1. where can i donate an office desk and sofa
- 2. where to donate for bahamas melbourne
- 3. how to donate to homeless veterans
- 4. how soon can you donate plasma after having covid
- 5. where can i donate clothing to veterans in massachusetts
- 6. where to donate second hand toys
- 7. how much sperm do i need to donate
- 8. where to donate food in seattle
- 9. where to donate clothing in brooklyn
- 10. how to donate to the medical and ammuition red dead 2