Bacterial electron transport chains
- Electron donors. In the present day biosphere, the most common electron donors are organic molecules. Organisms that use organic molecules as an electron source are called organotrophs.
- Complex I and II. Bacteria can use a number of different electron donors. ...
- Quinone carriers. Quinones are mobile, lipid-soluble carriers that shuttle electrons (and protons) between large, relatively immobile macromolecular complexes embedded in the membrane.
- Proton pumps. A proton pump is any process that creates a proton gradient across a membrane. ...
- Cytochrome electron carriers. Cytochromes are pigments that contain iron. They are found in two very different environments. ...
- Terminal oxidases and reductases. When bacteria grow in aerobic environments, the terminal electron acceptor (O 2) is reduced to water by an enzyme called an oxidase.
- Electron acceptors. Just as there are a number of different electron donors (organic matter in organotrophs, inorganic matter in lithotrophs), there are a number of different electron acceptors, both organic ...
What are the components of electron transport chain?
Jun 05, 2012 · The reduced NAD and FAD donate the electrons of the hydrogen atoms they are carrying to the first molecule in the electron transport chain.
What are the reactants and products of electron transport chain?
The reduced coenzymes generated by the citric acid cycle donate electrons in a series of reactions called the electron transport chain. The energy from the electron transport chain is used for oxidative phosphorylation.
What are the waste products of the electron transport chain?
The reduced coenzymes generated by the citric acid cycle donate electrons in a series of reactions called the electron transport chain. The energy from the electron transport chain is used for oxidative phosphorylation.
Which product is made by the electron transport chain?
Which of the following statements about the electron transport chain is true? (A) NADH and FADH2 donate their electrons to the chain. (B) Water is the last electron acceptor. (C) Electrons gain energy as they move down the chain. (D) The electron transport chain is the first step in cellular respiration.
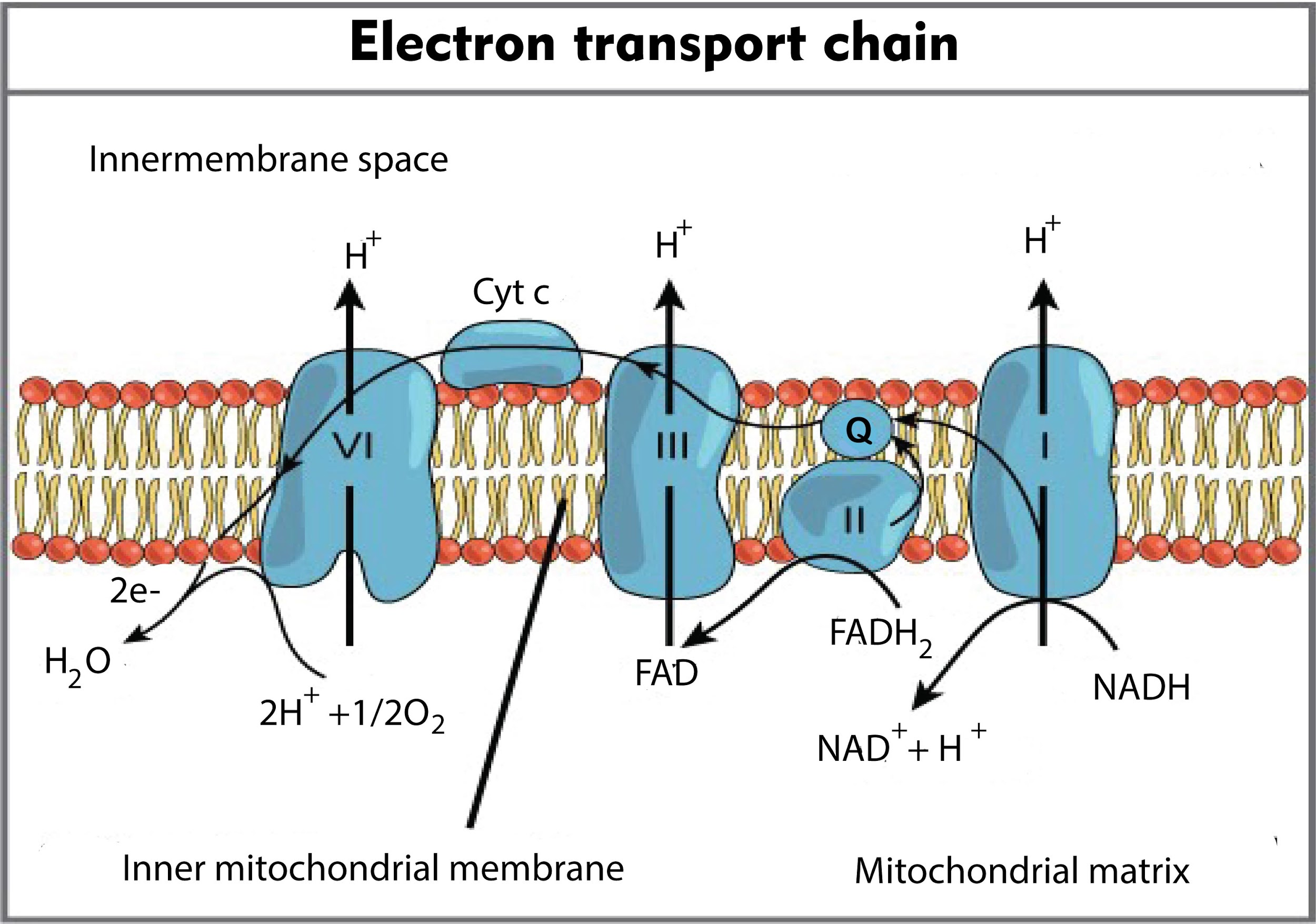
What is the electron transport chain?
The electron transport chain (ETC), or respiratory chain, is linked to proton movement and ATP synthesis. Select the statements that accurately describe the electron transport chain. Choose all that apply. Electron carriers are organized into four complexes of proteins and prosthetic groups.
Which amino acids are non-essential?
Non-essential amino acids. alanine, arginine, asparagine, aspartate, cysteine, glutamate, glutamine, glycine, proline, serine, tyrosine. Two of the 20 commonly occurring amino acids contain a sulfur atom. Identify the most direct source of the sulfur atom in these amino acids in humans. homocysteine.
What is the first stage of cellular respiration?
REASON: Glycolysis is the first stage in cellular respiration and does not depend on the presence of oxygen. Identify all correct statements about the basic function of fermentation. (A) The basic function of fermentation is the production of additional ATP by further oxidation of the products of glycolysis.
Does glycolysis produce carbon dioxide?
There is no production of carbon dioxide in glycolysis. Which of the following is the best explanation for this fact? (A) There is very little ATP produced in glycolysis. (B) The products of glycolysis contain the same total number of carbon atoms as in the starting material.
Is cellular respiration exergonic or exergonic?
This is because cellular respiration is an exergonic process that is only about 38% efficient; the remaining energy is lost to the environment as heat. Also, carbon dioxide is being converted to organic molecules such as fats and sugars during cellular respiration.

Popular Posts:
- 1. where can i donate eyeglasses at costco
- 2. how to donate copper shield riders of icarus
- 3. how many times can you donate plasma
- 4. where can i donate children's clothes near me
- 5. donate plasma how much
- 6. how to donate money online
- 7. what if i can't donate on my regular day at octapharma
- 8. what charities does bill gates donate to
- 9. where can i donate covid antibodies
- 10. how often can we donate platelets