Bacterial electron transport chains
- Electron donors. In the present day biosphere, the most common electron donors are organic molecules. Organisms that use organic molecules as an electron source are called organotrophs.
- Complex I and II. Bacteria can use a number of different electron donors. ...
- Quinone carriers. Quinones are mobile, lipid-soluble carriers that shuttle electrons (and protons) between large, relatively immobile macromolecular complexes embedded in the membrane.
- Proton pumps. A proton pump is any process that creates a proton gradient across a membrane. ...
- Cytochrome electron carriers. Cytochromes are pigments that contain iron. They are found in two very different environments. ...
- Terminal oxidases and reductases. When bacteria grow in aerobic environments, the terminal electron acceptor (O 2) is reduced to water by an enzyme called an oxidase.
- Electron acceptors. Just as there are a number of different electron donors (organic matter in organotrophs, inorganic matter in lithotrophs), there are a number of different electron acceptors, both organic ...
Which reduced coenzymes donate electrons to the electron transport chain?
Jun 05, 2012 · The reduced NAD and FAD donate the electrons of the hydrogen atoms they are carrying to the first molecule in the electron transport chain.
What are the products of the electron transport chain?
The reduced coenzymes generated by the citric acid cycle donate electrons in a series of reactions called the electron transport chain. The energy from the electron transport chain is used for oxidative phosphorylation.
What is the role of cytochromes in electron transport chain?
The reduced coenzymes generated by the citric acid cycle donate electrons in a series of reactions called the electron transport chain. The energy from the electron transport chain is used for oxidative phosphorylation.
What is the electron transport chain of the citric acid cycle?
a) FADH2 would be the main electron donor to the electron transport chain instead of NADH. b) Electrons would start to flow in the opposite direction, converting water into O2 and H+. c) H2O would be made instead of O2 at the end of the chain. d) Cyt a 3 prosthetic groups would remain oxidized and Cyt a would have nowhere to donate electrons. e) FMN prosthetic groups would …
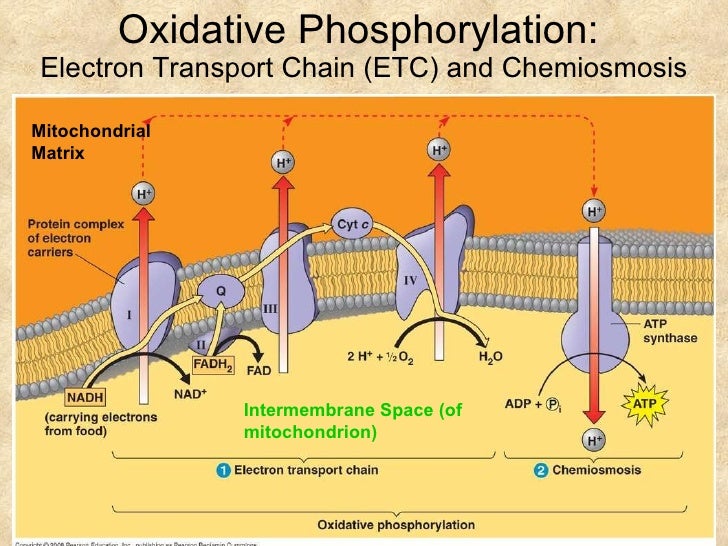
What is the electron transport chain?
The electron transport chain (ETC), or respiratory chain, is linked to proton movement and ATP synthesis. Select the statements that accurately describe the electron transport chain. Choose all that apply. Electron carriers are organized into four complexes of proteins and prosthetic groups.
Which group is directly involved in electron transfer?
Prosthetic groups, such as iron-sulfur centers, are directly involved with electron transfer. Without using a textbook, predict the sequence of electron transport carriers (the sequence of participants in the redox reactions) in the electron transport chain.
What is the function of cytosolic malate dehydrogenase?
Cytosolic malate dehydrogenase: reduces OAA to malate, oxidizes NADH produced in glycolysis to NAD+, transfers reducing equivalents from cytosolic NADH to a molecule that can traverse the inner mitochondrial membrane.
What would happen if an uncoupling agent, such as 2,4-dinitrophenol, was added to
Predict what would happen when an uncoupling agent, such as 2,4-dinitrophenol, is added to an actively respiring tissue preparation. Ingestion of uncouplers causes profuse sweating and an increase in body temperature. Explain this phenomenon in molecular terms. The rate of oxygen consumption would increase.
What will happen if ATP levels are low in mutant yeast cells?
Low ATP levels will maintain the high rate of glucose consumption in the mutant yeast cells. In the absence of cytochrome oxidase, oxidative phosphorylation will be inhibited and ATP production will decrease drastically. Low ATP levels will maintain the high rate of glucose consumption in the mutant yeast cells.
How many repetitions are needed for 14 carbon myristic acid?
Therefore, the synthesis of the 14-carbon myristic acid requires six repetitions.
How do hydrogen ions enter the mitochondrial matrix?
Hydrogen ions enter the mitochondrial matrix via facilitated diffusion. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are unstable, or reactive, compounds that result from the partial reduction of oxygen. ROS can cause damage to molecules, including membrane lipids and nucleic acids, and may be associated with some diseases.
Popular Posts:
- 1. which of the blood samples tested could donate to a person with type a+ blood?
- 2. where to donate a horse tucson
- 3. where to donate old couch
- 4. how much can you donate without a receipt
- 5. how do i donate my sperm
- 6. where to donate toya
- 7. country where citizens donate the most?
- 8. where can i donate my testicle
- 9. how much blood can a dog donate
- 10. where to donate a car in idaho